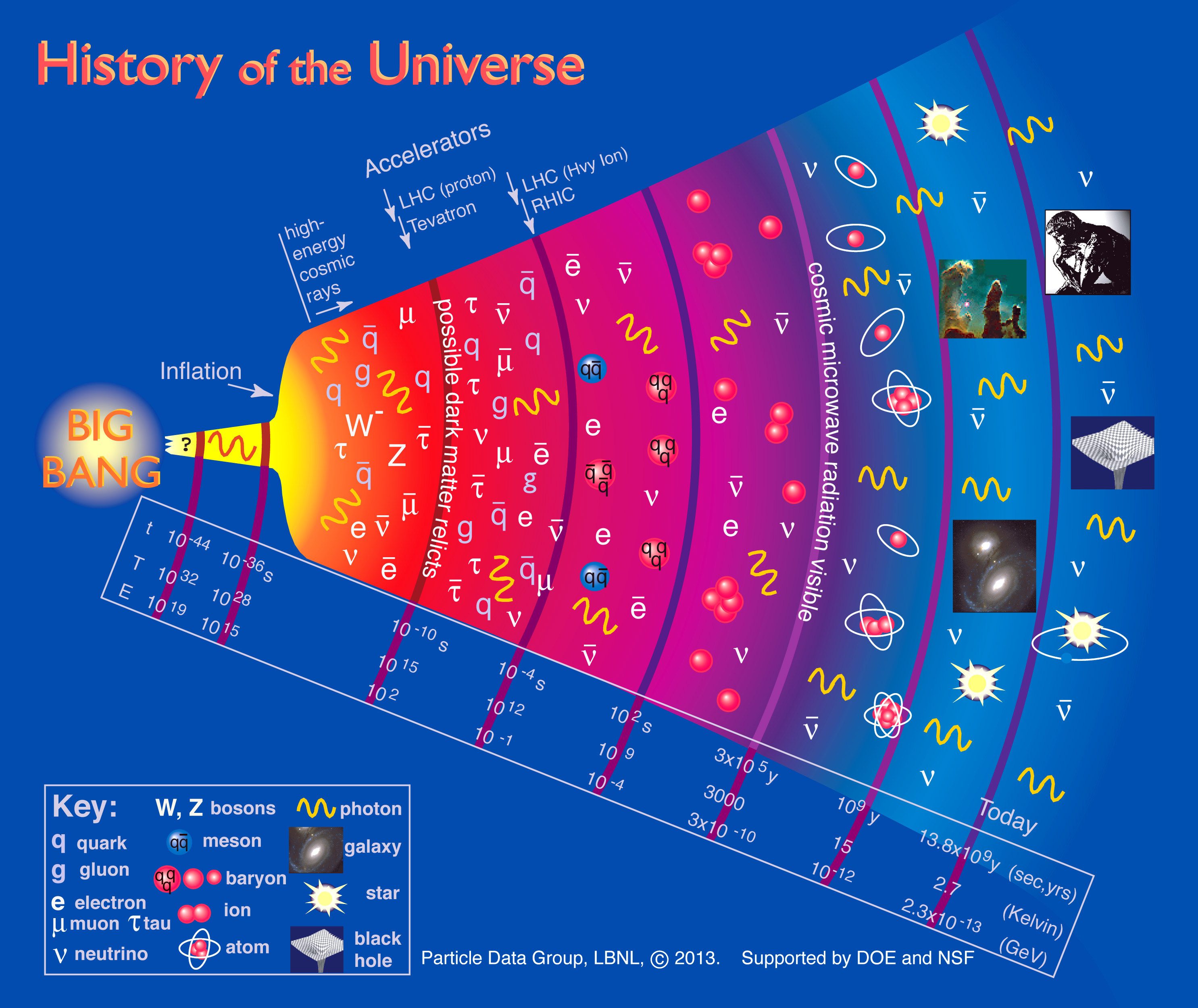
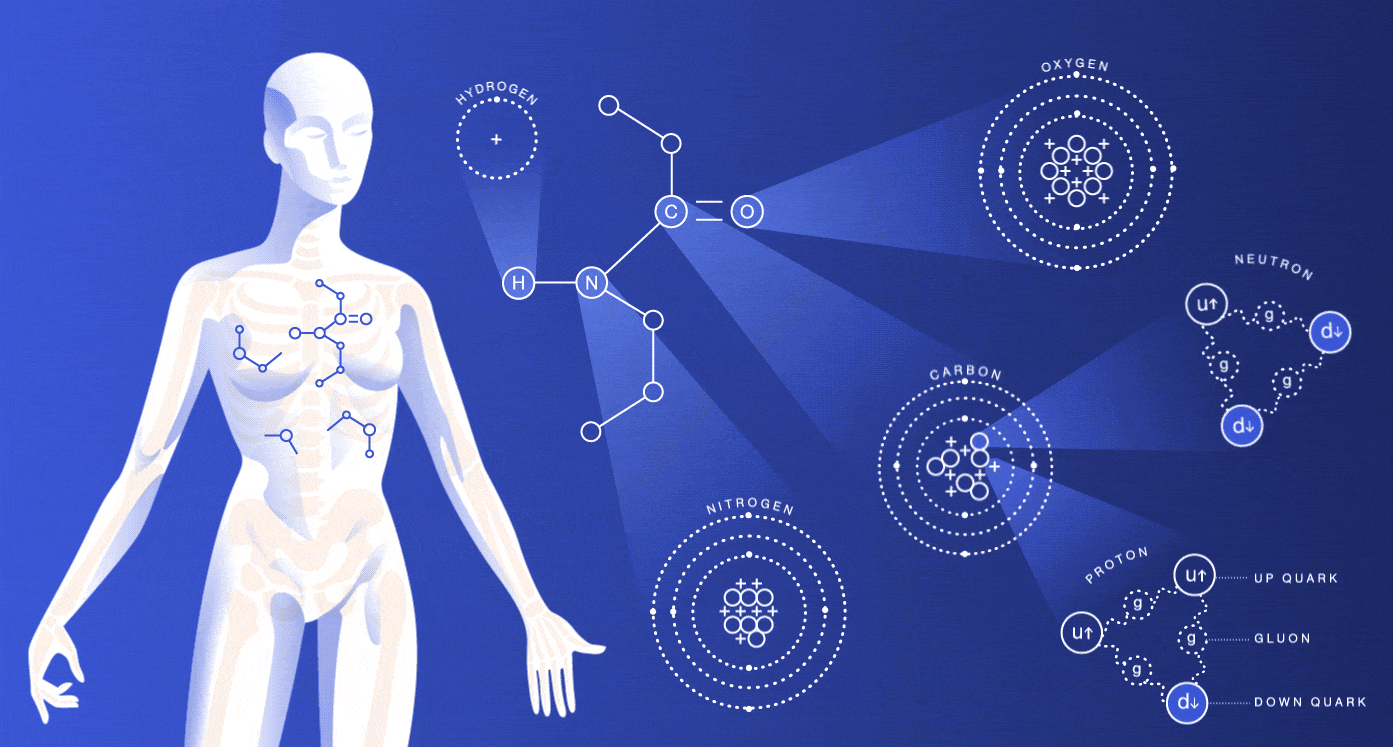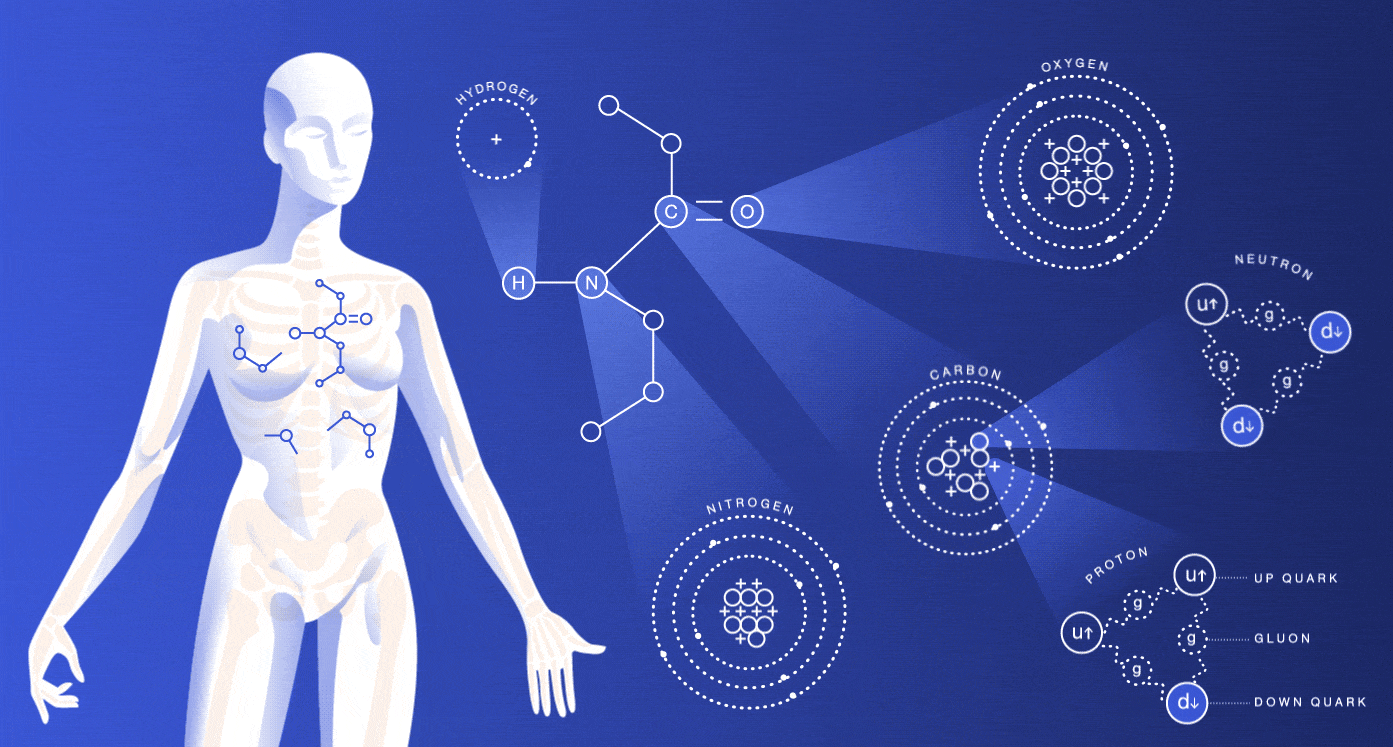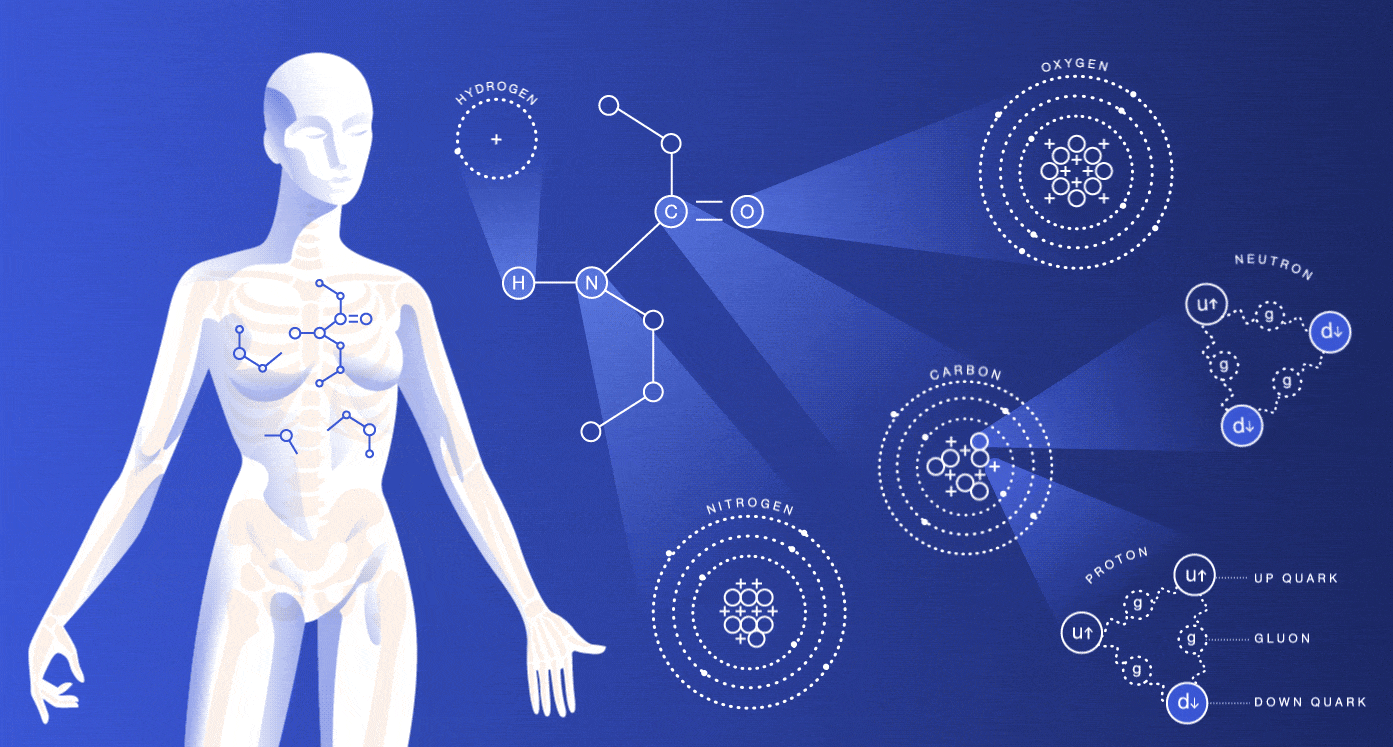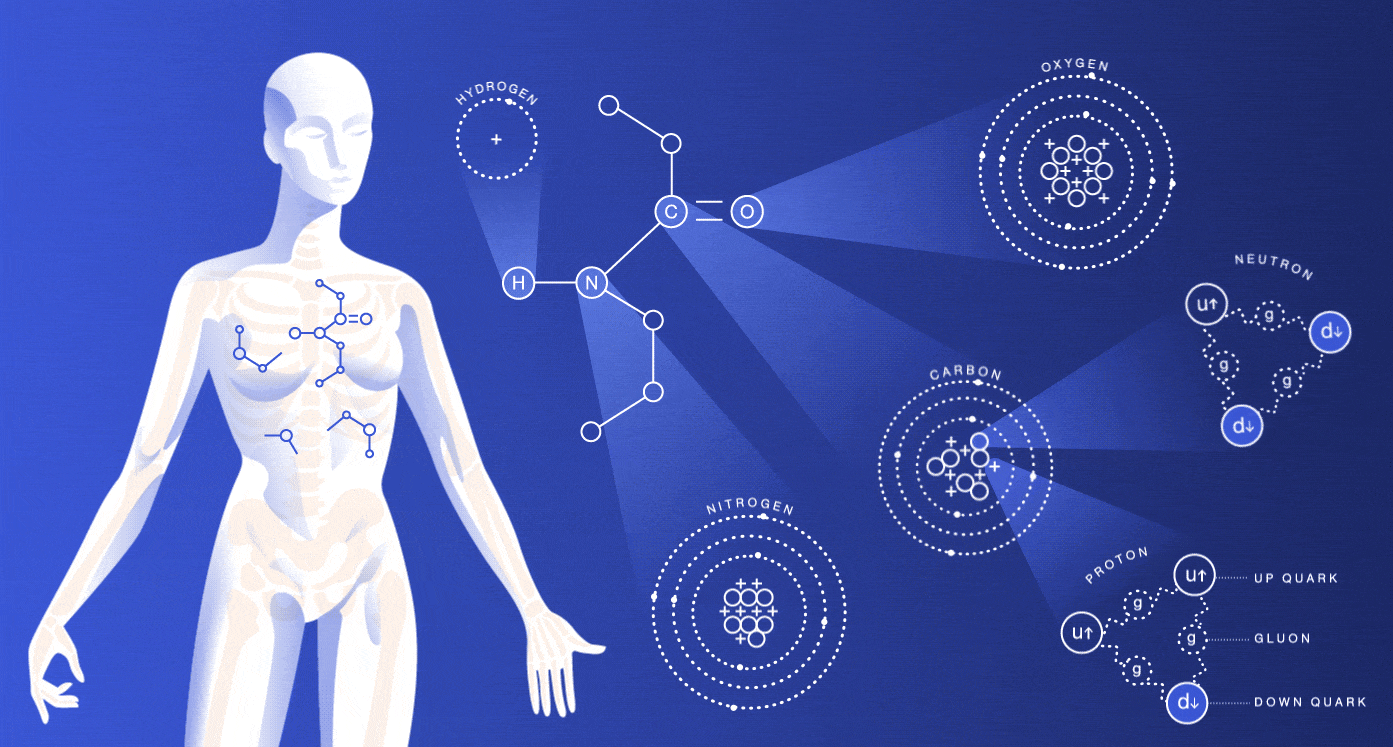
Research topics are classified into Simulation, Data analysis, and Instrumentation
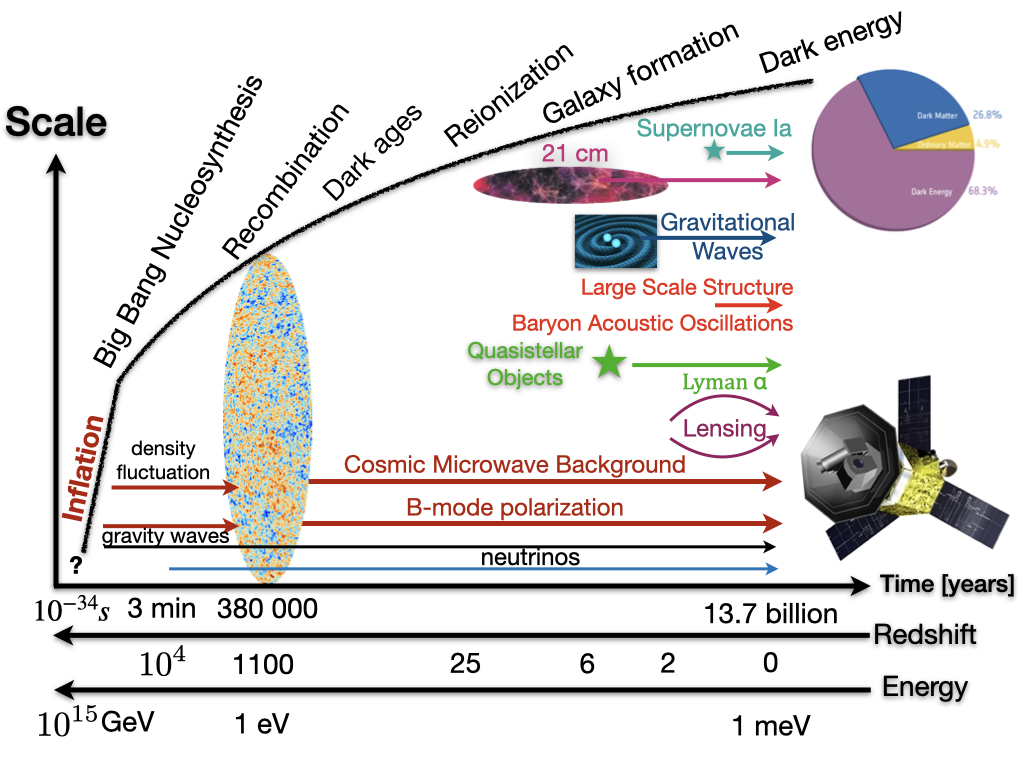
I have been contributing to several Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) projects such as LiteBIRD, QUBIC, simons Observatory (SO), CMB-S4, and BICEP. Future CMB projects aim to measure polarization signal that imprint primordial gravitational waves from the Early Universe in the context of the Big Bang theory. I am curious in roles magnetic fields and star formation processes.Summary of my experiences:
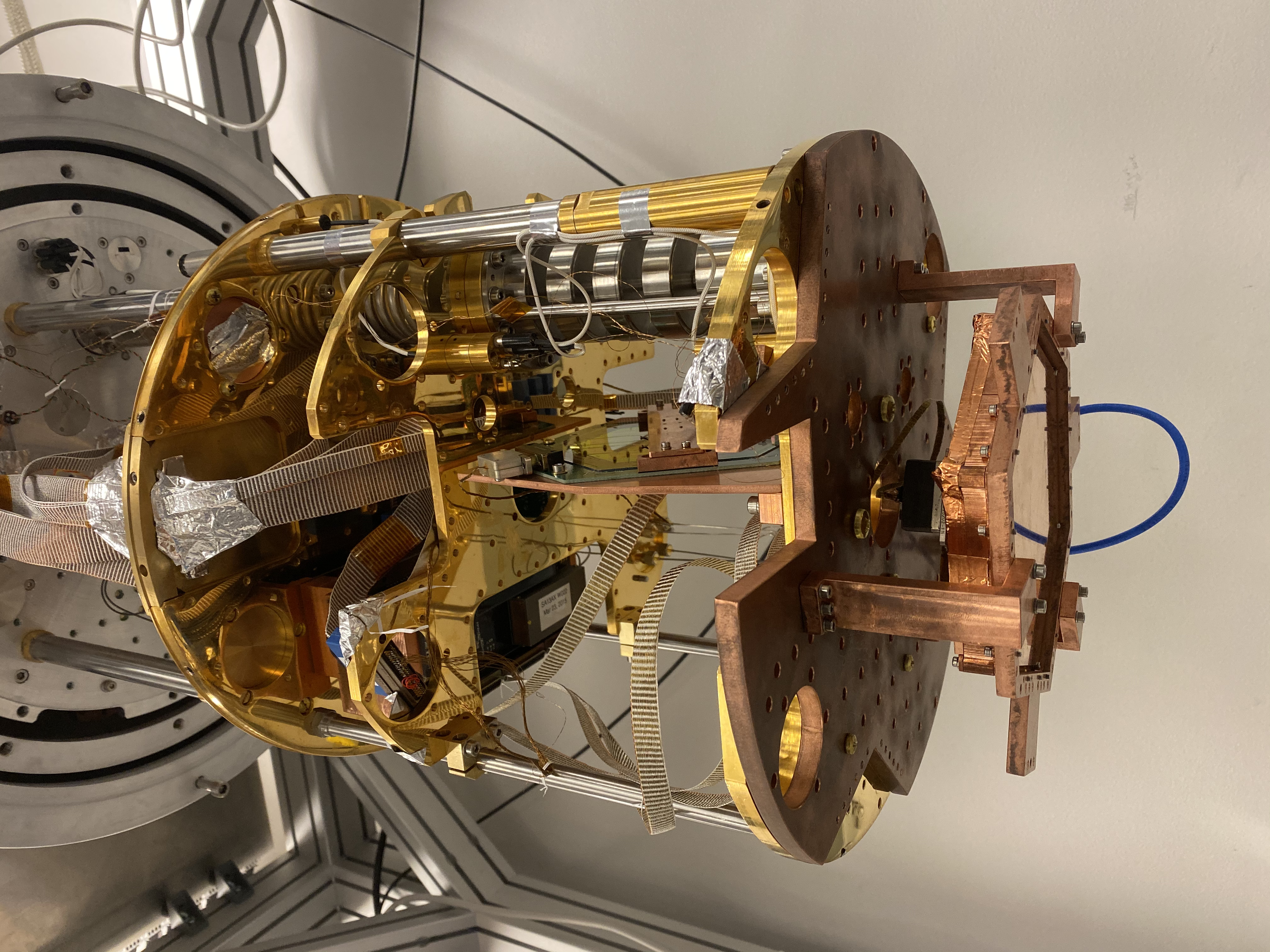
7. LiteBIRD: Desmonstration of a small prototype polarization modulator for LiteBIRD low-frequency telescope.
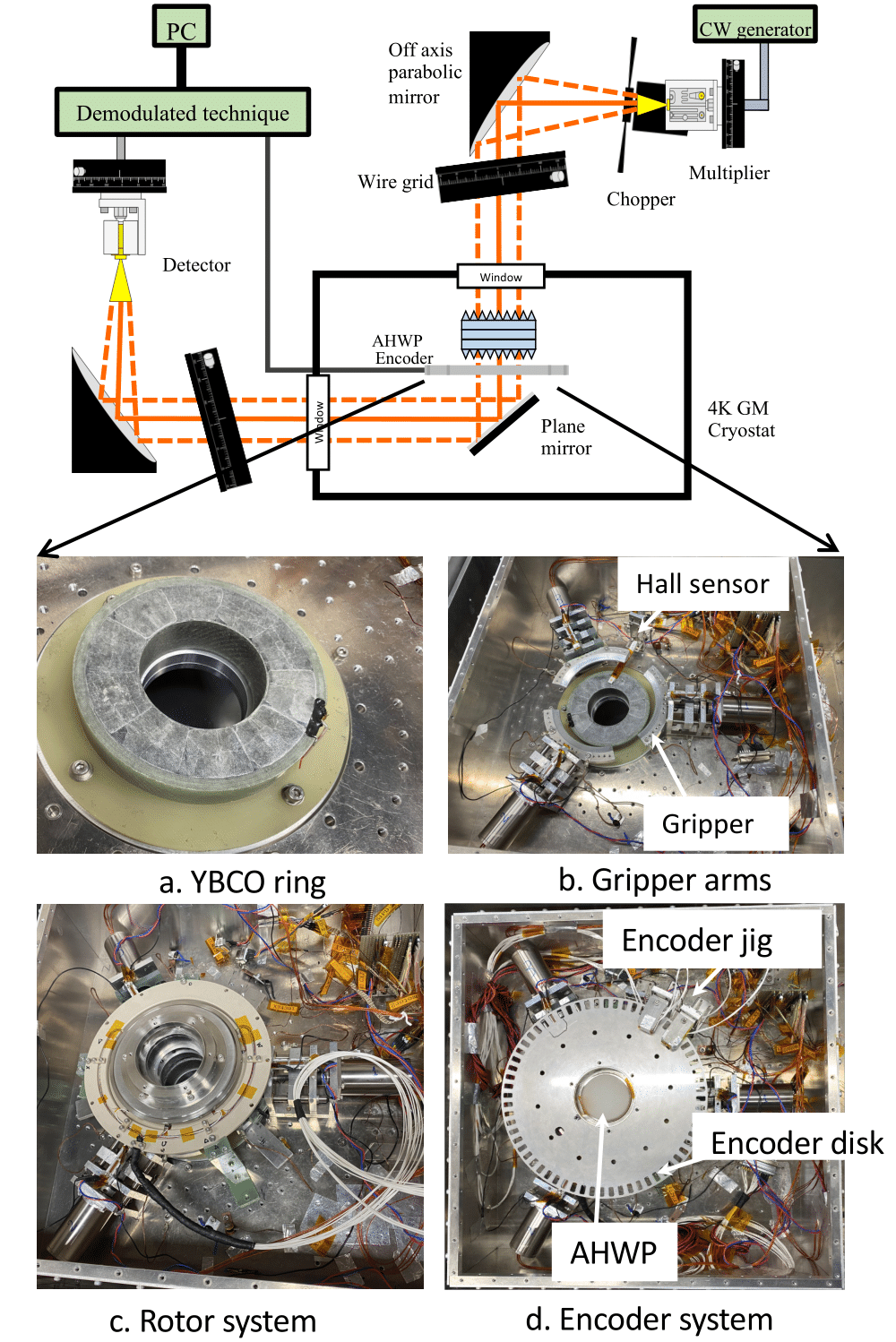
In this study, the entire PMU system was cooled to 10 K in a cryostat chamber using a 4-K Gifford-McMahon cooler. A coherent millimeter-wave polarized signal was passed through the rotating HWP and the resulting modulated signal was detected. The AHWP modulated optical signal and rotational synchronous signals from the rotational mechanism were analyzed . The testbed was built to integrate the broadband HWP PMU and assess potential systematic effects in the optical data, paving the way for a full-scale model.
This study is published in the SPIE proceeding [ SPIE ]. I recored a video of the full prototype PMU system testbed in Liquid Nitrogen (77 K), the PMU is levitated and spun [ HWP levitation]
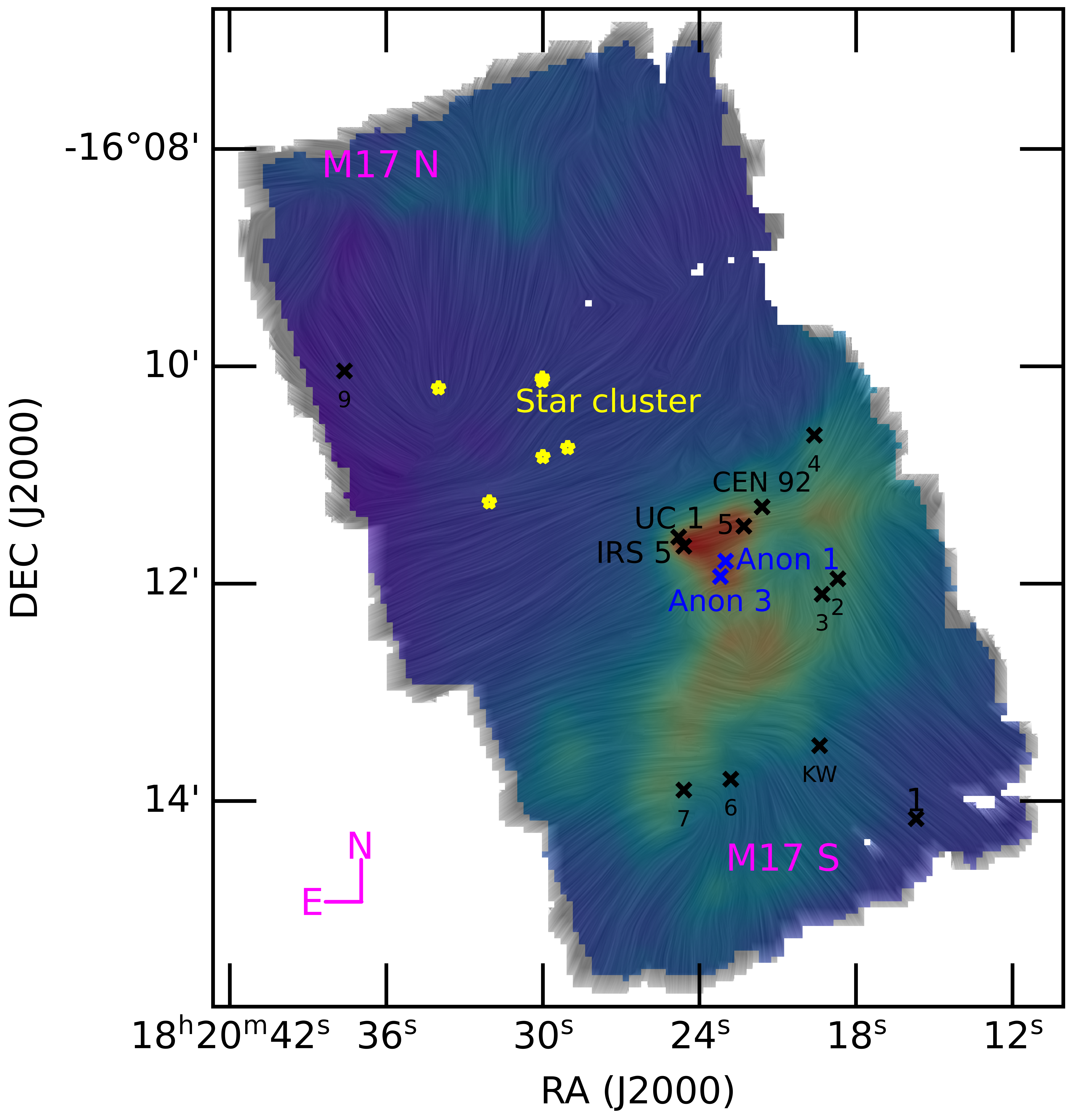
6. SOFIA: Magnetic fields toward M17 cloud.
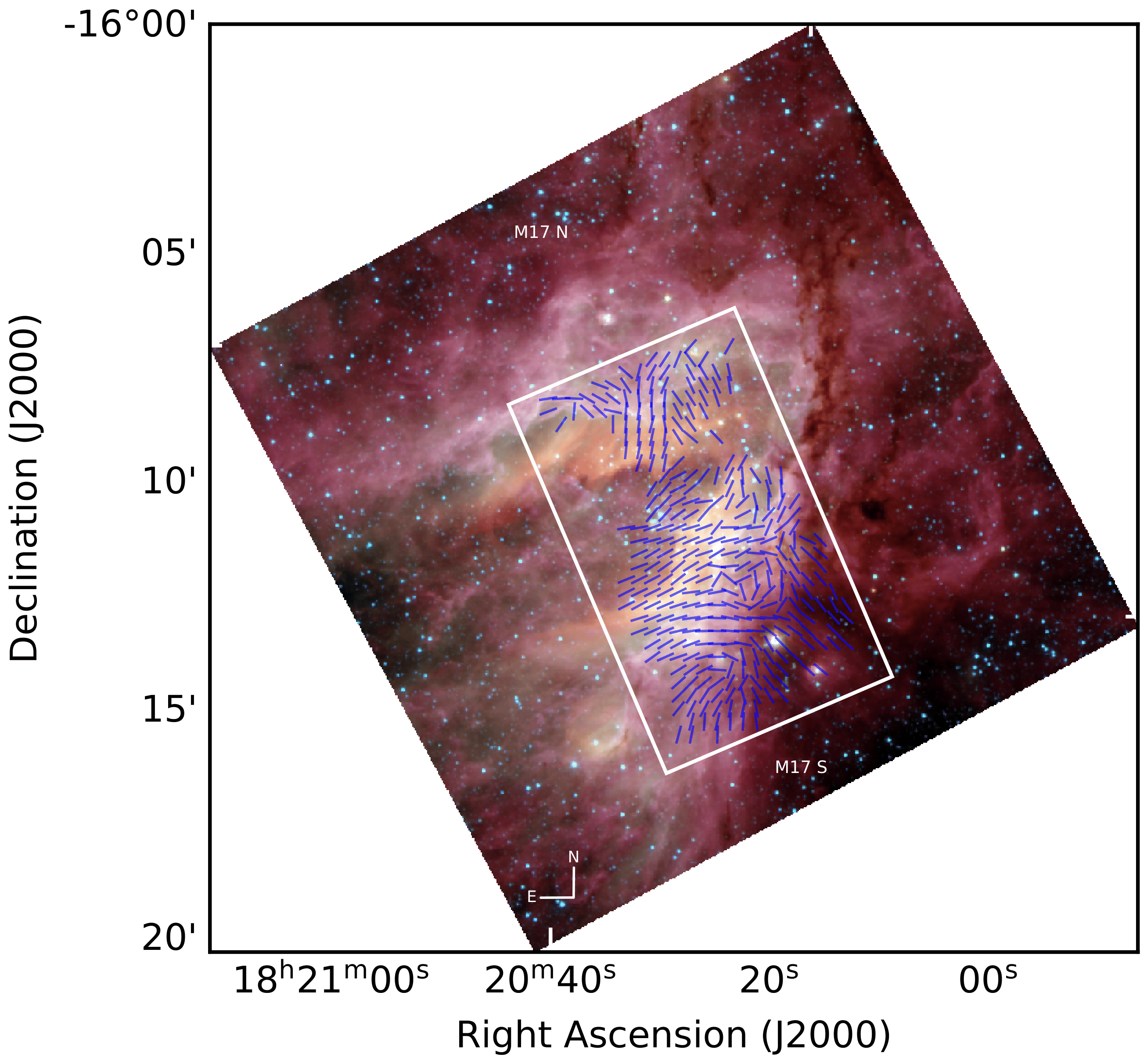
This study presents the measurement of the component of magnetic fields in the plane- of-sky of the M17 region using thermal dust polarization data obtained with SOFIA/HAWC+ at 154 μm wavelength. The DCF method was used to determine the presence of strong magnetic fields of approximately 327 ± 34 μG and 839 ± 80 μG in lower- and higher-density regions, respectively. The gravitational mass-to-magnetic flux ratio was also calculated, and the relative contributions of B-fields and turbulence in the M17 region were examined. In addition, the alignment of dust grains in this region was investigated using the radiative torque paradigm.
The study is published in the ApJ journal [ arxiv:2108.10045 ]
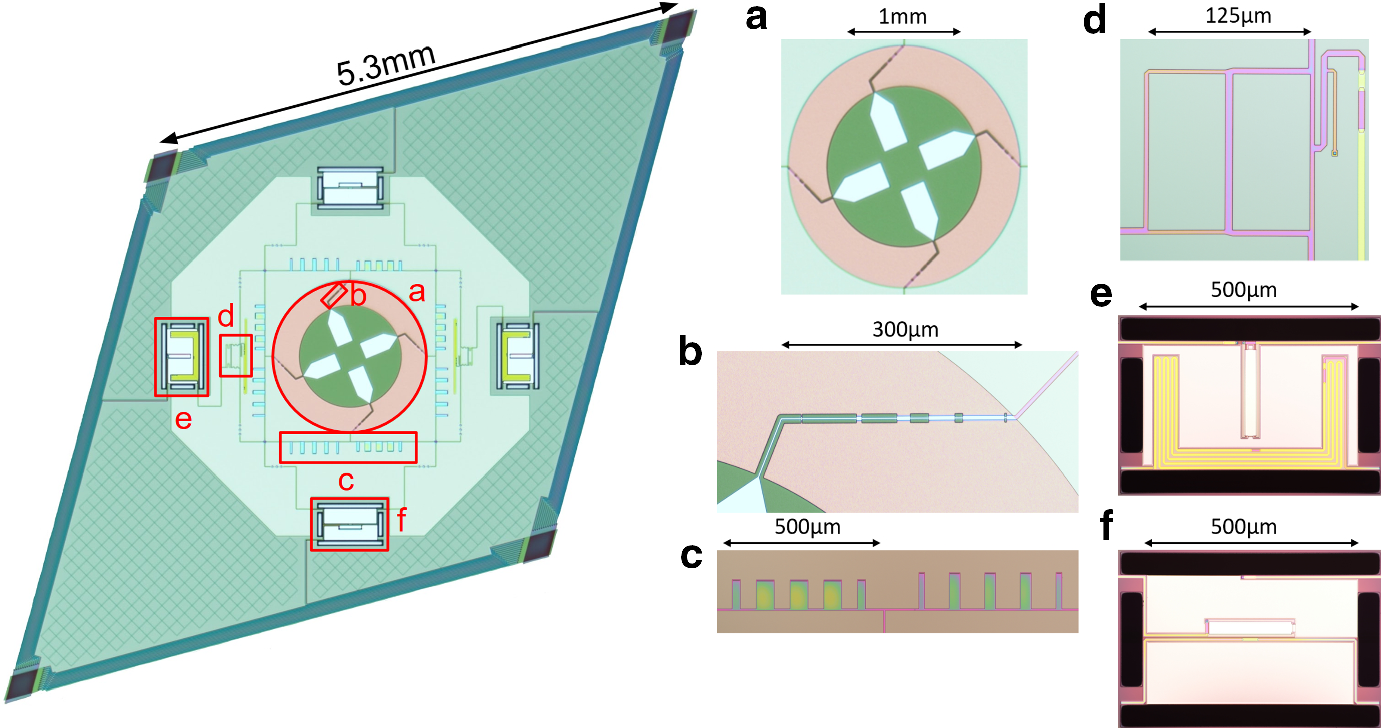
5. Simons Observatory (SO): Testbed focal plane.
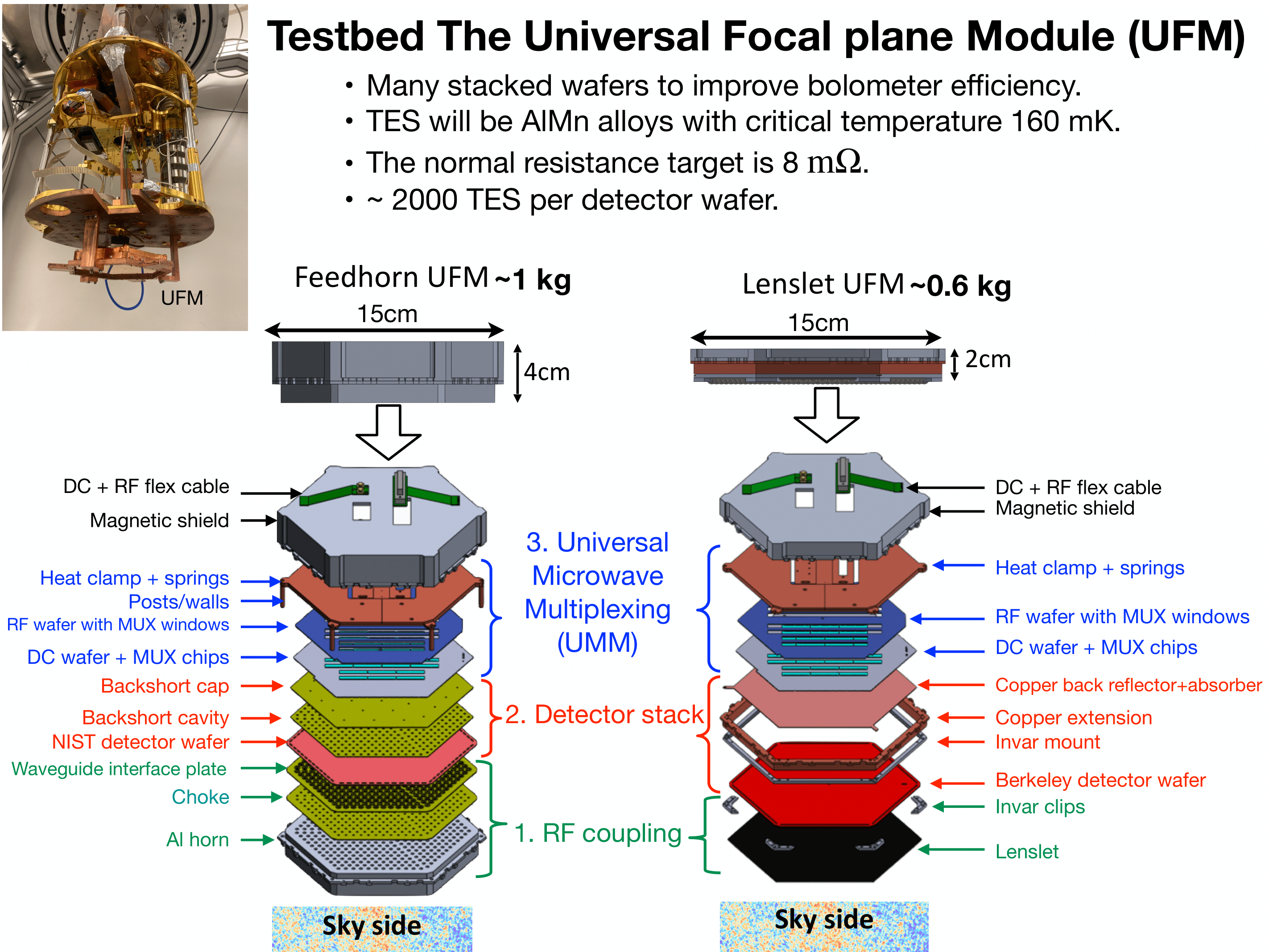
I have been working on the testbed system for the readout chain and UMM of the UFM:
A study of external magnetic fields and the SO's readout system SQUID is published in [ arXiv:2012.04532 ]
4. LiteBIRD: Systematic effects.

Bandpass mismatch error is one of the important systematic effects that can affect thecurrent and next-generation measurements of the polarization of the Cosmic Micro wave Background radiation (CMB). The slightly different frequency bandpasses among detectorsintroduce leakage from intensity into CMB polarization.
Using full focal plane simulations, I evaluated the level of this effect for future CMB satellite missions and estimated of its possible impact on the final determination of the tensor-to-scalar ratio r . I have simulated thetime streams with filter variations as observed in the Planck HFI. I assumed nominal scanning strategies and detector parameters for LiteBIRD. I projected data using the simplest map-making coaddition method. Power spectra of residual EE and BB coming from the leakage maps are computed for 80 % sky fraction excluding the galactic plane. The amplitude of leakage depends on the scanning strategy of the satellite parameterized with precession angle, spin angle, precession spin and rotating spin. The conclusion of this work is that the spurious angular power spectrum could potentially bias r for measurements of the reionization bump, and of the recombination bump. The bandpass mismatch effect is negligible in case of an ideal HWP.
The study is published in JCAP [ arXiv:1706.09486 ]
3. QUBIC: Calibrated Transition Edge Sensor (TES) array with a radioactive source.
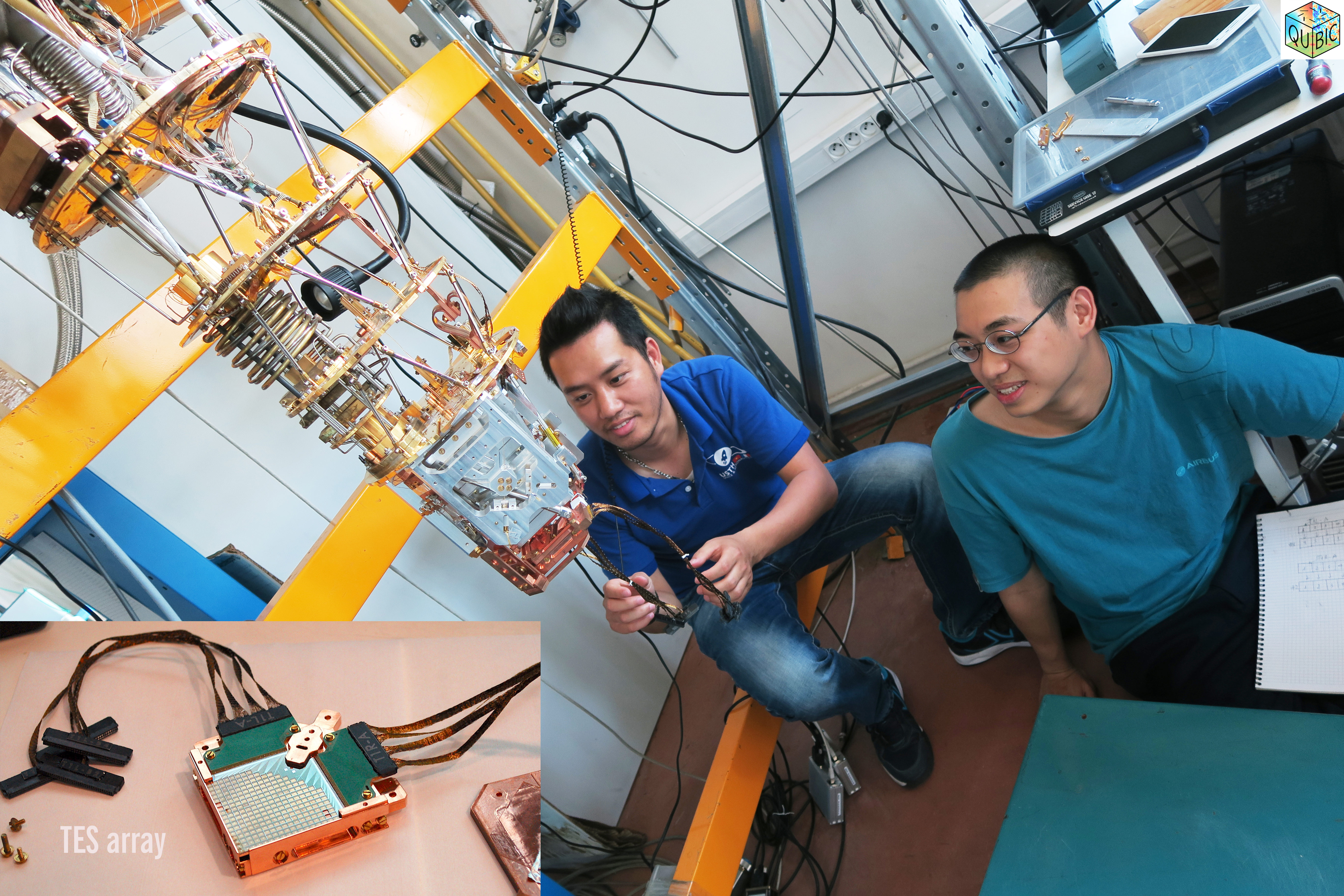
An 241 Americium radioactive source is set up in front of the 256-TES array in the mixing chamber inside the cryostat cooling down to background temperature Tb=300 mK. When particles hit a TES pixel, the deposited energy could be transformed to temperature elevation of the TES components (eg: Thermometer, absorbing grid, substrate) and also affect the neighbor pixels that provides a possible measurement of the cross-talk among pixels.
This study allows us to understand the thermal time constant (30-60 ms) of a TES and the readout system time constant (10-20ms) .
The study is published in [ https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2312080 ], and [ arXiv:2101.06787 ]
2. CMB-S4: Survey strategy at Atacama-Chile.
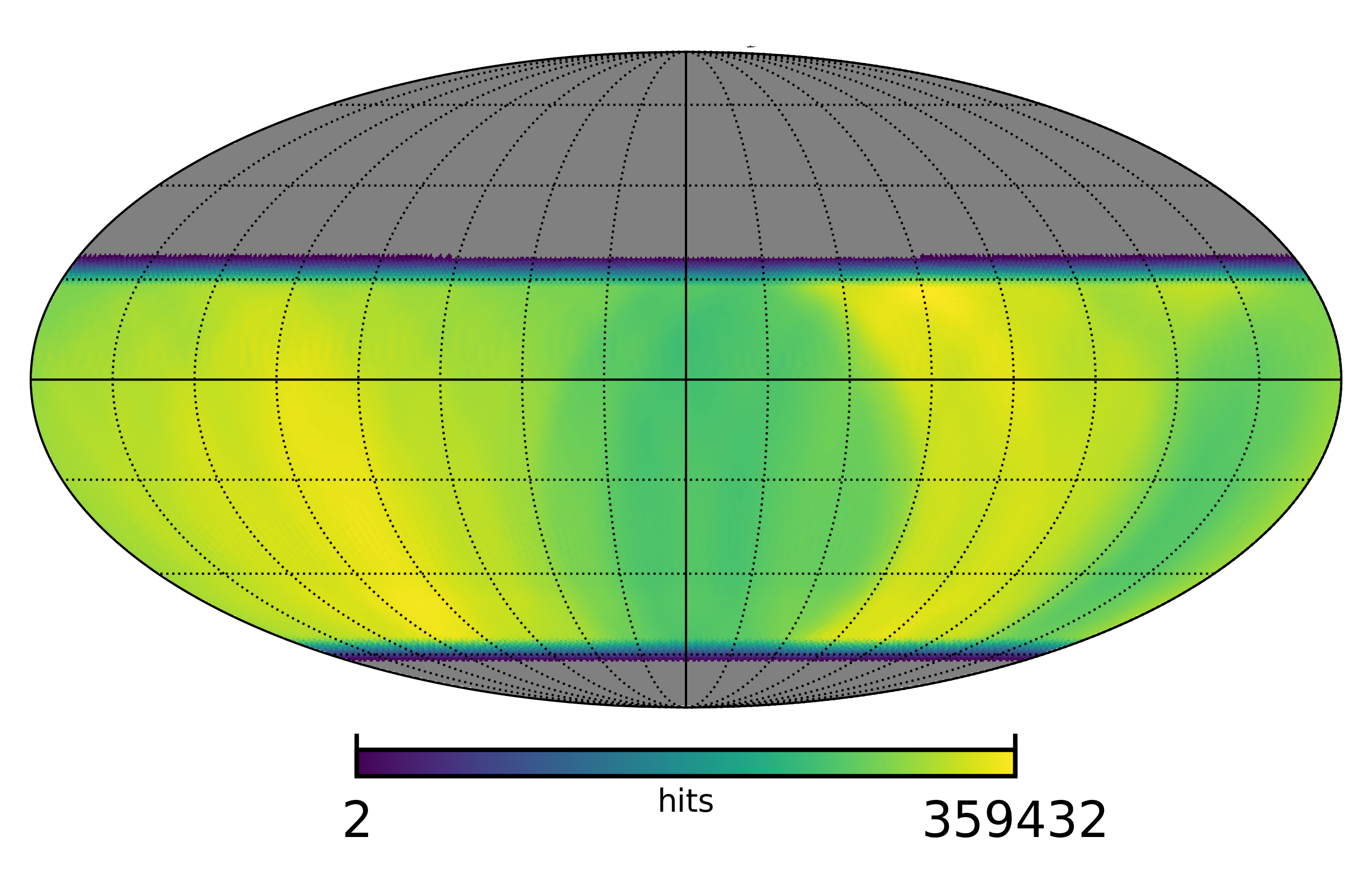
I have been studying the optimization strategies for telescopes located at the Atacama Desert site (SO, CMB-S4, CCAT: Cerro Chajnantor Atacama Telescope) using the Time Ordered Astrophysics Scalable Tools ( TOAST T) installed at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC). In my study, TOAST is used to simulate a hardware configuration of a typical telescope then create a sky observation. The resulted observational schedule and hit count maps of detectors can be used to evaluate the depth, efficiency, and uniformity of the survey strategy.
The detail study of CMB-S4 Large Aperture Tescope (LAT) at Chile is written in CMB-S4 website [ Modulate scan high cadence LAT ].
1. Planck: Bolometer and Cosmic Rays.
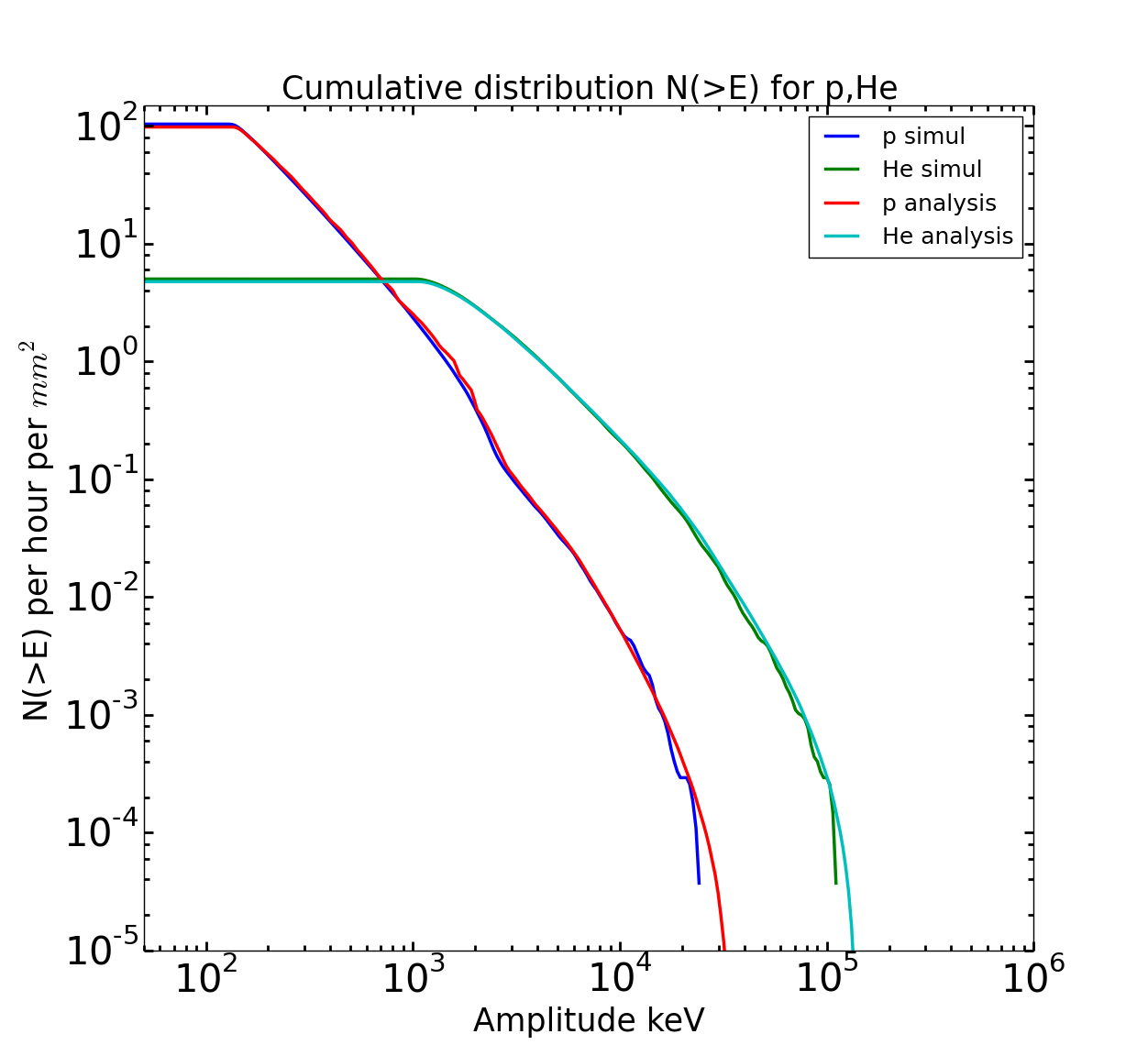
I developed a simple model of the interaction of galactic particles with the silicon die of the Planck bolometers. I predicted the number of events per deposit energyd due to primary cosmic rays particles. I have observed good agreements between the analytical approach and the Monte Carlo simulation method.
Basing on this experienced study with Planck, I had been studying the interaction of cosmic rays with the focal plane of the LiteBIRD mission.
Master thesis [ pdf ].
Publications
Google ScholarSummary research: